
Home automation is the automatic control of electronic devices in your home.
These devices are connected to the Internet, which allows them to be controlled
remotely. With home automation, devices can trigger one another so you don’t
have to control them manually via an app or voice assistant. For example, you can
put your lights on schedules so that they turn off when you normally go to sleep, or
you can have your thermostat turn the A/C up about an hour before you return to
work so you don’t have to return to a stuffy house. Home automation makes life
more convenient and can even save you money on heating, cooling and electricity
bills. Home automation can also lead to greater safety with Internet of Things
devices like security cameras and systems. But hold up; what’s the Internet of
Things?
Alexa, turn on the lights! We don’t know about your home, but in our home, most
things are automated; our lights turn on whenever we’re nearby, our coffee starts
making itself in the morning, and our security system disarms whenever we’re
almost home. Not only are these features convenient, but they also save us energy
and thus, money on utility bills. But since home automation is a relatively new
technology, some people may find it overwhelming. Here, we’re breaking down
exactly what home automation is and how you can add some to your life. Believe us,
the process is much less complicated than it may seem.

How Does Home Automation Work?
Home automation works via a network of devices that are connected to the Internet
through different communication protocols, i.e Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, and others.
Through electronic interfaces, the devices can be managed remotely through
controllers, either a voice assistant like Alexa or Google Assistant or an app. Many of
these IoT devices have sensors that monitor changes in motion, temperature and
light so the user can gain information about the device’s surroundings. To make
physical changes to the device, the user triggers actuators, the physical mechanisms
like light switches, motorized valves or motors that allows devices to be
controlled remotely.1
Home automation works on three levels:
Monitoring: Monitoring means that users can check in on their devices remotely
through an app. For example, someone could view their live feed from a smart
security camera.

Nest Hello and Google Home Hub
Control: Control means that the user can control these devices remotely, like
panning a security camera to see more of a living space.

Amazon Echo Show and Box
Automation: Finally, automation means setting up devices to trigger one another,
like having a smart siren go off whenever an armed security camera detects motion.
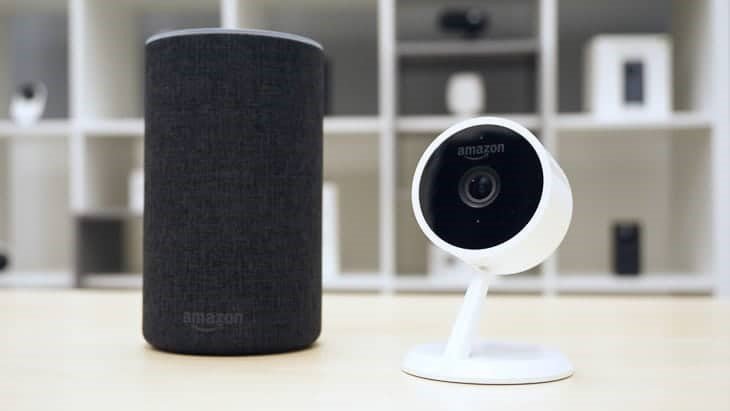

Amazon Alexa and Amazon Cloud Cam
Remote Control
The hallmark of home automation is remote control, which is done through either a
mobile application or through a voice assistant.
Mobile Application: The mobile application allows users to control their devices in
real-time, whether it’s shutting off the outdoor lights or opening the garage door for
a neighbor. The app is also where users set schedules, create scenes, groups of IoT
devices, and customize device settings, like having your living room lights set to the
perfect shade of blue. Most of the IoT devices we’ve reviewed have apps for
Android and iOS devices, making them compatible with the majority of mobile
devices and tablets.
Voice Assistants: If home automation is the sundae, think of voice assistants as the
cherry on top. With voice assistants, you can use your voice to control devices,
whether that’s disarming a security system as you walk in the front door, showing
your video doorbell’s footage on your Echo Show device, or setting a timer on a
smart speaker while your hands are full of cooking utensils. Most IoT devices work
with one of three voice assistants: Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri.
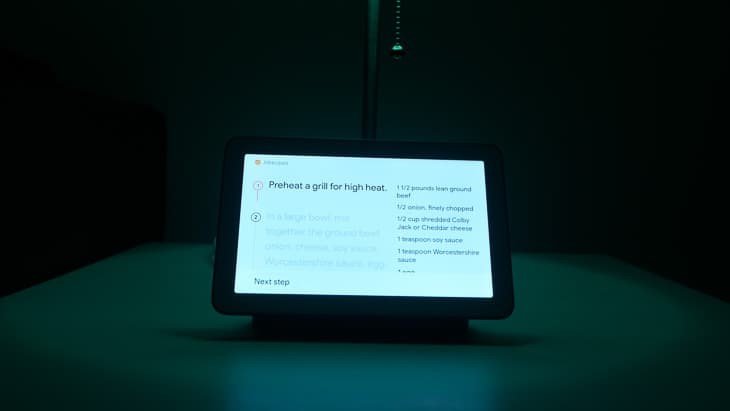
Recipes on the Google Nest Hub
Answered Correctly Understood Query
Alexa 79.80% 99.90%
Google Assistant 92.90% 100%
Siri 83.10% 99.80%
Loup Ventures Annual Digital Assistant IQ Test Results2
Alexa: Alexa is Amazon’s voice assistant that’s built into Echo Show and Echo Dot
devices (for more information, check out our Echo Show review and our Echo Dot
with Clock review). Alexa is the voice assistant we see integrated into the highest
number of smart home devices from companies like SimpliSafe, Ring Alarm and
Vivint.

Amazon Alexa
Google Assistant: Google Assistant, is, as you can imagine, Google’s voice assistant.
Although Google Assistant has fewer “skills” or “actions” than Alexa, it has been
proven to be the most accurate voice assistant in terms of understanding and
answering queries correctly. To get Google Assistant, you’ll need a smart speaker or
a smart display; read our Nest Mini review or Nest Hub review to get started.

Google Nest Mini
Siri: Siri is Apple’s voice assistant that’s integrated into the iPhone. While Siri holds
35 percent of the global market share for voice assistants, compared to nine percent
and four percent with Google Assistant and Alexa,3 respectively, there aren’t too
many IoT devices that work with Siri. Rather, the voice assistant is used mainly on
iPhones and iPads in contrast to home automation devices, where Alexa and Google
Assistant reign supreme.
Control Protocols
The way that IoT devices connect to the Internet and each other is their control
protocol; if IoT devices are people, think of the protocol as their common languages.
Like on Earth, there are a few different languages, or protocols, that devices can
speak, including:
WiFi: WiFi is by far the most common control protocol; it means that your IoT device
will use the regular Internet provided by your Internet Service Provider. While this
doesn’t require an additional hub, note that it can slow your web surfing speeds
down, especially if you have a ton of different IoT devices set up at once.
Z-Wave: Don’t want to mess with your home’s WiFi? Z-Wave is a wireless
technology that won’t interfere with your WiFi; rather, it operates on low power at
908.42 Mhz in the U.S and Canada.5
ZigBee: Similar to Z-Wave, ZigBee is a mesh network and universal language that
lets IoT devices communicate.
Thread: Thread is another low-power, wireless mesh networking protocol based on
an IP address open standard; it lets IoT devices connect to each other and the cloud.
Bluetooth: Finally, Bluetooth is another mesh technology that lets people control
and monitor IoT devices and automate systems.
For most people, WiFi-connected devices will be sufficient, but for more advanced
smart homes, you might want to switch to a mesh network like Z-Wave or ZigBee.